Git is a distributed version control system widely used for tracking changes in source code during software development. It was created by Linus Torvalds in 2005 and has since become the standard for version control in the software development industry. Here are some key concepts and features of Git:
Version Control System (VCS): Git allows developers to keep track of changes made to their codebase over time. It records every change made to files, making it easy to revert to previous versions if needed.
Distributed System: Unlike centralized version control systems, Git is distributed. Each developer has a complete copy of the repository, including its full history. This makes it more robust and flexible, as developers can work independently and merge changes later.
Repository: A Git repository is a collection of files and directories associated with a project, along with the entire history of changes made to those files.
Commit: A commit is a snapshot of the changes made to the code at a specific point in time. Developers create commits to record their work and provide a history of the project.
Branching: Git allows developers to create branches to work on new features or bug fixes independently of the main codebase. Branches can be merged back into the main branch when the work is complete.
Step 1: Generate an SSH key pair
If you do not have an existing SSH key pair, generate a new one:
Open a Linux terminal.
Run
ssh-keygen -tfollowed by the key type and an optional comment. This comment is included in the.pubfile that’s created.For example, for RSA:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 2048 -C "comment"
- Press Enter. Output similar to the following is displayed:
Generating public/private ed25519 key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/user/.ssh/id_ed25519):
Press Enter again( Optional: You can set passphrase here)
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again:vim ~/.ssh/configHost: mention your Hostname
IdentityFile - location of private key
# GitLab.com
Host gitlab.com
PreferredAuthentications publickey
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/gitlab_com_rsa
Add SSH keys to Gitlab
Login to you Gitlab account
Go to Profile --> Preferences --> SSH Keys
Choose Preferences --> SSH Keys
Add new SSH key
Copy the public key from your linux machine (copy from ssh-rsa )
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABgQCt6uYrAPG2Bu6foMJp9N9lZ+KjDmfVKfETxp
bvYa43xu6EIAU/zjM0zxZ23Z/zs9sgv6G9pHs/Z/fsn4J3sQVfUBeJ/JryDLsNoGF+SXfszHRGq
Ln5Gh6CCSviEze48dPyvbzePyxGA305T+8Zw82m6mj/e85U7YyckME8wyclawbi+rFQDjDpLEDB
q9X/2Paj58RIJ8ScC1A3qpPR8g7e/xW6E2QBVkb5PsrGtfaRagpY+ySwTqIvApTCmOT9jrRnMj
GwzVWdzOKw3I/ywdPTztxQwFvOhRRbPNVVXcsmBYD5tT4aGe2Zx6Gc3snBv1ez+s883fqz2Xad
SxyeDBZg+c1eAN+Ouqp9QadKWS+hs/pWPp6kicx6mGjY4ygkA+bFHJ7a+kRBY6GQ7NgX6vTYAW
cQ9eKZFW+UsA4E7rPbQkfXJ8i/pzb/y12HOwBEh/0sBhhrSE1RvEVOcADjW2+r0yA5wnTKCYsCMG
9VON6UB7p/GiZ6ww9w9J5eB44+ksE= test1@ubuntu22
And paste on Github like Below , Add your own Title
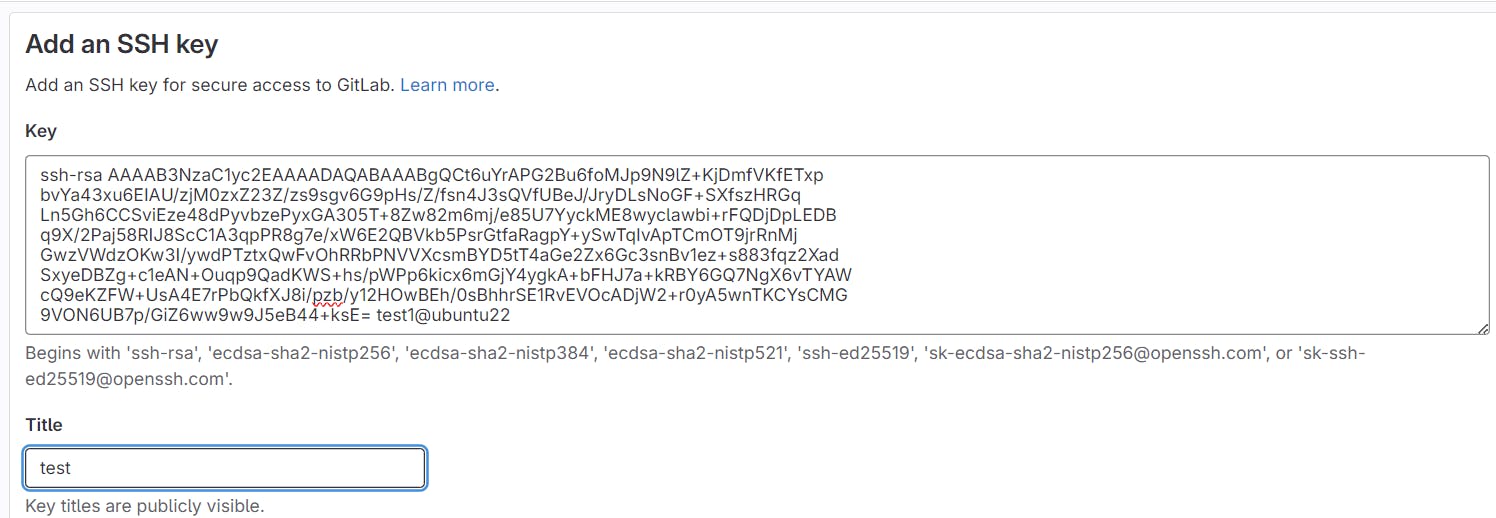
- Then click Add Key.
Verify that you can connect
ssh -T git@gitlab.example.com
Type yes and Press Enter
The authenticity of host 'gitlab.example.com (192.168.11.153)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:HbW3g8zUjNSksFbqTiUWPWg2Bq1x8xdGUrliXFzSnUw.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Git clone Repository
Copy the Clone link from you Repo
Choose Clone with SSH
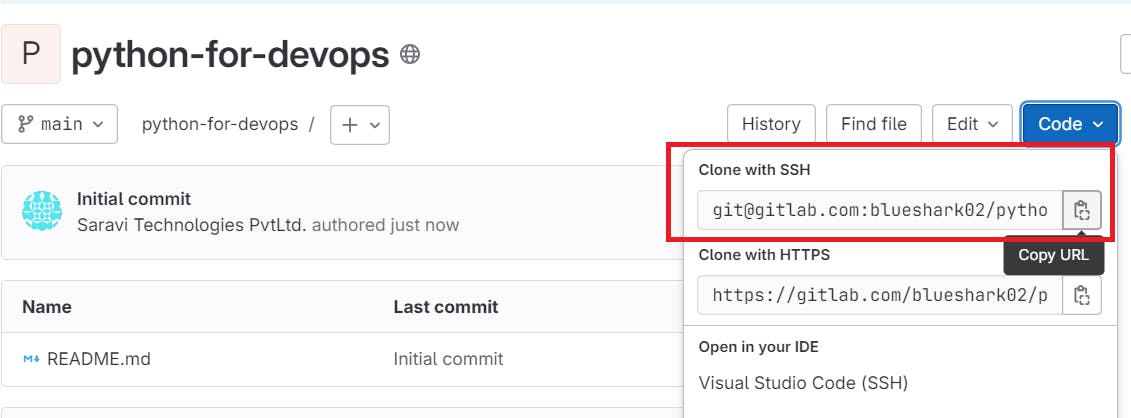
ex: https://gitlab.com/blueshark02/python-for-devops.git
git clone https://gitlab.com/blueshark02/python-for-devops.git
Setup Git set Remote
git remote set-url origin https://gitlab.com/blueshark02/python-for-devops.git
git git branch -M main
git push -uf origin main
First Commit to Gitlab
echo "test file" > test.file
# Add to stage
git add .
# Commit the file
git commit -m "comments"
# Push to remote
git push
# check log
git log
#check remote repo
git remote -v
Follow for more: ✌️
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/karthick-dkk
Medium: karthidkk123.medium.com
Github: github.com/karthick-dkk


